Neutron
The
neutron
is a
subatomic particle
, symbol
n
or
n
0
, with no net
electric charge
and a
mass
slightly larger than that of a
proton
. Protons and neutrons constitute the
nuclei
of
atoms
. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, and each has a mass of approximately one
atomic mass unit
, they are both referred to as
nucleons
.
[5]
Their properties and interactions are described by
nuclear physics
.
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
309036 characters 38 sections 90 paragraphs 14 images 582 internal links 134 external links |
neutron 0.602 neutrons 0.580 fission 0.176 nuclear 0.150 protons 0.123 proton 0.118 energy 0.116 quarks 0.108 nuclei 0.102 decay 0.093 nucleus 0.092 mev 0.090 quark 0.075 atomic 0.071 electron 0.068 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic particle
, symbol
|
|
| 2017 |
292637 characters 38 sections 90 paragraphs 13 images 512 internal links 130 external links |
neutron 0.601 neutrons 0.582 fission 0.175 nuclear 0.149 protons 0.123 proton 0.117 energy 0.115 quarks 0.107 nuclei 0.102 decay 0.096 nucleus 0.095 mev 0.095 quark 0.074 atomic 0.070 electron 0.068 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic particle
, symbol
|
|
| 2016 |
282945 characters 38 sections 88 paragraphs 13 images 504 internal links 103 external links |
neutron 0.600 neutrons 0.577 fission 0.180 nuclear 0.151 protons 0.118 quarks 0.116 proton 0.112 nuclei 0.112 energy 0.110 mev 0.102 decay 0.093 nucleus 0.091 quark 0.076 magnetic 0.072 beta 0.069 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic particle
, symbol
|
|
| 2015 |
252603 characters 38 sections 81 paragraphs 13 images 490 internal links 85 external links |
neutrons 0.594 neutron 0.591 fission 0.192 nuclear 0.153 nuclei 0.119 protons 0.114 proton 0.114 energy 0.112 mev 0.109 decay 0.102 nucleus 0.097 beta 0.073 electron 0.071 atomic 0.071 nuclide 0.069 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic particle
, symbol
|
|
| 2014 |
268277 characters 42 sections 94 paragraphs 12 images 508 internal links 84 external links |
neutrons 0.601 neutron 0.550 fission 0.180 nuclear 0.151 nucleus 0.140 protons 0.135 nuclei 0.130 proton 0.120 energy 0.113 decay 0.099 mev 0.098 atomic 0.094 electron 0.085 beta 0.081 electrons 0.070 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic particle
, symbol
|
|
| 2013 |
177704 characters 33 sections 64 paragraphs 9 images 416 internal links 54 external links |
neutrons 0.687 neutron 0.485 fission 0.197 nuclear 0.136 protons 0.124 nucleus 0.123 nuclei 0.113 energy 0.098 mev 0.089 decay 0.085 reactors 0.081 fusion 0.072 proton 0.071 beta 0.068 electron 0.067 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic
hadron
particle that has the symbol
|
|
| 2012 |
170971 characters 33 sections 65 paragraphs 9 images 413 internal links 50 external links |
neutrons 0.679 neutron 0.490 fission 0.206 nuclear 0.139 protons 0.124 nucleus 0.124 nuclei 0.119 energy 0.090 mev 0.087 decay 0.085 reactors 0.085 fusion 0.075 beta 0.072 proton 0.071 electron 0.071 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic
hadron
particle which has the symbol
|
|
| 2011 |
143299 characters 30 sections 54 paragraphs 8 images 401 internal links 34 external links |
neutrons 0.697 neutron 0.497 fission 0.197 nuclei 0.129 protons 0.129 nuclear 0.121 nucleus 0.100 reactors 0.089 fusion 0.086 energy 0.077 radiation 0.069 atomic 0.068 ħ 0.066 reactor 0.063 mev 0.057 |
The
neutron
is a
subatomic
hadron
particle which has the symbol
|
|
| 2010 |
122650 characters 30 sections 54 paragraphs 7 images 364 internal links 20 external links |
neutrons 0.685 neutron 0.515 fission 0.200 nuclei 0.131 nuclear 0.126 protons 0.111 nucleus 0.095 reactors 0.090 fusion 0.087 energy 0.081 radiation 0.070 ħ 0.067 nuclides 0.066 atomic 0.064 capture 0.060 |
The neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton . With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons . The number of protons in a nucleus is the atomic number and defines the type of element the atom forms. The number of neutrons is the neutron number and determines the isotope of an element. For example, the abundant carbon-12 isotope has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while the very rare radioactive carbon-14 isotope has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. |
|
| 2009 |
106963 characters 27 sections 50 paragraphs 6 images 332 internal links 11 external links |
neutrons 0.728 neutron 0.462 fission 0.194 nuclei 0.130 protons 0.112 nuclear 0.097 reactors 0.095 energy 0.083 fusion 0.078 nucleus 0.075 radiation 0.073 mev 0.067 epithermal 0.065 decay 0.064 atomic 0.062 |
The neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton . |
|
| 2008 |
95077 characters 26 sections 47 paragraphs 4 images 307 internal links 8 external links |
neutrons 0.728 neutron 0.437 fission 0.200 reactors 0.127 nuclei 0.110 nuclear 0.103 energy 0.097 nucleus 0.091 protons 0.090 radiation 0.079 decay 0.078 beta 0.074 free 0.073 quarks 0.072 antineutrino 0.068 |
The neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton . |
|
| 2007 |
67285 characters 18 sections 26 paragraphs 4 images 258 internal links 8 external links |
neutrons 0.631 neutron 0.506 protons 0.147 nucleus 0.135 radiation 0.110 beta 0.109 proton 0.108 nuclei 0.108 nuclear 0.105 quarks 0.085 isotope 0.083 atomic 0.078 antineutrino 0.075 antineutron 0.075 gamma 0.075 |
In physics , the neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass of 939.573 MeV / c ² or 1.008 664 915 (78) u (1.6749 × 10 −27 kg, slightly more than a proton ). Its spin is ½. Its antiparticle is called the antineutron . The neutron, along with the proton , is a nucleon . |
|
| 2006 |
55239 characters 15 sections 24 paragraphs 3 images 239 internal links 6 external links |
neutron 0.611 neutrons 0.480 nuclear 0.132 protons 0.122 proton 0.119 quarks 0.117 radiation 0.114 nuclei 0.112 antineutron 0.104 electron 0.101 nucleus 0.093 decay 0.087 beta 0.086 isotope 0.077 gamma 0.074 |
In physics , the neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass of 939.573 MeV / c ² (1.6749 × 10 -27 kg, slightly more than a proton ). Its spin is ½. Its antiparticle is called the antineutron . The neutron, along with the proton, is a nucleon . |
|
| 2005 |
47858 characters 14 sections 23 paragraphs 1 images 221 internal links 4 external links |
neutron 0.564 neutrons 0.543 nucleus 0.154 protons 0.150 proton 0.138 antineutron 0.128 nuclear 0.121 nuclei 0.103 3he 0.096 gamma 0.096 radiation 0.088 particles 0.085 ionization 0.085 elastic 0.083 energy 0.083 |
In physics , the neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass of 939.573 MeV / c ² ( 1.6749 -27 kg, slightly more than a proton ). Its spin is ½. Its antiparticle is called the antineutron . The neutron and proton are instances of a nucleon . |
|
| 2004 |
12982 characters 3 sections 7 paragraphs 0 images 66 internal links 0 external links |
neutron 0.473 neutrons 0.369 uncharged 0.294 nucleus 0.220 charged 0.156 proton 0.152 gamma 0.151 protons 0.138 nuclear 0.134 nuclei 0.126 particles 0.125 joliot 0.118 radiation 0.112 penetrating 0.103 free 0.097 |
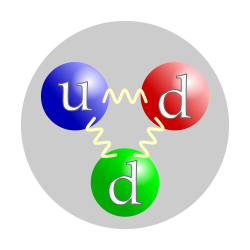
In physics , the neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass of 940 MeV / c 2 ( 1.6749 -27 kg, slightly more than a proton ). Its spin is 1/2. The nucleus of most atoms (all except the most common isotope of Hydrogen , which consists of a single proton only) consists of protons and neutrons. Outside the nucleus, neutrons are unstable and have a half-life of about 15 minutes, decaying by emitting an electron and antineutrino to become a proton. The same decay method ( beta decay ) occurs in some nuclei. Particles inside the nucleus are typically resonances between neutrons and protons, which transform into one another by the emission and absorption of pions . A neutron is classified as a baryon , and consists of two down quarks and one up quark . The neutron's antimatter equivalent is the antineutron . |
|
| 2003 |
8869 characters 2 sections 8 paragraphs 0 images 47 internal links 0 external links |
neutrons 0.400 neutron 0.353 uncharged 0.318 nucleus 0.239 charged 0.169 gamma 0.164 protons 0.149 nuclear 0.145 proton 0.137 nuclei 0.136 particles 0.136 subatomic 0.135 penetrating 0.112 radiation 0.104 beryllium 0.103 |
In physics , the neutron is a subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass of 940 MeV (very slightly more than a proton ). The nucleus of most atoms (all except the most common isotope of Hydrogen , which consists of a single proton only) consists of protons and neutrons. Outside the nucleus, neutrons are unstable and have a half-life of about 15 minutes, decaying by emitting an electron and antineutrino to become a proton. The same decay method ( beta decay ) occurs in some nuclei. Particles inside the nucleus are typically resonances between neutrons and protons, which transform into one another by the emission and absorption of pions . A neutron is classified as a baryon , and consists of two down quarks and one up quark . |
|
| 2002 |
8482 characters 2 sections 9 paragraphs 0 images 43 internal links 0 external links |
neutrons 0.408 neutron 0.359 uncharged 0.324 nucleus 0.243 charged 0.173 gamma 0.167 protons 0.152 nuclear 0.148 proton 0.140 nuclei 0.139 particles 0.138 penetrating 0.114 radiation 0.106 beryllium 0.104 atoms 0.090 |
The neutron is a particle of neutral electric charge and approximately the same mass as the proton . The nucleus of most atoms (all except the most common isotope of Hydrogen , which consists of a single proton only) consists of protons and neutrons. Outside the nucleus, neutrons are unstable and have a half-life of about 15 minutes, decaying by emitting an electron and antineutrino to become a proton. The same decay method ( beta decay ) occurs in some nuclei. Particles inside the nucleus are typically resonances between neutrons and protons, which transform into one another by the emission and absorption of pions . A neutron is classified as a baryon , and consists of two down quarks and one up quark . |
|
| 2001 |
3340 characters 0 sections 10 paragraphs 0 images 13 internal links 0 external links |
uncharged 0.284 gamma 0.243 radiation 0.233 1932 0.185 proton 0.184 neutrons 0.179 protons 0.166 penetrating 0.166 nucleus 0.152 particles 0.152 neutron 0.143 untenable 0.142 antineutrino 0.142 joliot 0.142 paraffin 0.142 |
A particle of neutral electric charge and approximately the same mass as the proton . Outside the nucleus of an atom it is unstable and has a half-life of about 15 minutes, decaying by emitting an electron and antineutrino to become a proton. The same decay method ( β-decay ) occurs in some nuclei. Particles inside the nucleus are typically resonances between neutrons and protons, which transform into one another by the emission and absorption of pions . A neutron contains two down quarks and one up quark . |